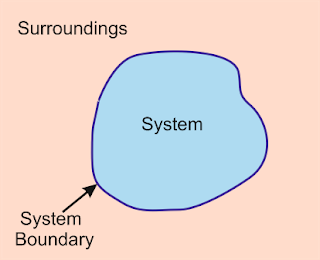
A thermodynamic system is referred to a quantity of matter or a volume in space in which one or more thermodynamic processes take place in reference to its surroundings and is used for their study and analysis. System surroundings are referred to everything outside system of system. A thermodynamic system is separated from its surroundings by the boundary. The boundary may be either real or imaginary and fixed or moving. A system, its boundary and its surrounding together form a universe.
TYPES OF THERMODYNAMIC SYSTEMS
There are three types of thermodynamic systems given below ;
- Open System
- Closed System, &
- Isolated System
Open Thermodynamic System
A thermodynamic system in which both mass and energy are allowed to transfer across system boundary is referred to as an open thermodynamic system. There may be flow of matter as well as energy into or out of the system. An example of open system is steam turbine where fluid or steam enters the turbine at high temperature & pressure and leaves turbine after thermodynamic process at low temperature and pressure.
Closed Thermodynamic System
A thermodynamic system in which only energy is allowed to transfer across the system boundary is referred to as a closed system. There may be flow of energy into or out of the system but no matter flow takes place across the system boundary. This is the system with fixed mass.
Isolated Thermodynamic System
A thermodynamic system in which neither mass nor energy is allowed to transfer across the system boundary is referred to as Isolated System. There is no interaction between system and its surroundings. Practically, these type of systems do not exist.



No comments:
Post a Comment